🚀 Perceiver IO for vision (learned position embeddings)
A Perceiver IO model pre - trained on ImageNet, which can be used for image classification and feature extraction for downstream tasks.
🚀 Quick Start
You can use the raw model for image classification. This model is pre - trained on ImageNet (14 million images, 1,000 classes) at a resolution of 224x224.
✨ Features
- Modality - agnostic: Perceiver IO is a transformer encoder model applicable to any modality such as text, images, audio, video, etc.
- Efficient self - attention: It employs self - attention on a small set of latent vectors, making the time and memory requirements independent of input size.
- Flexible decoding: Uses decoder queries to flexibly decode the final hidden states of the latents for outputs of arbitrary size and semantics.
- Direct pixel training: Can be trained directly on raw pixel values without relying on patches like ViT.
💻 Usage Examples
Basic Usage
from transformers import PerceiverFeatureExtractor, PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned
import requests
from PIL import Image
feature_extractor = PerceiverFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-learned")
model = PerceiverForImageClassificationLearned.from_pretrained("deepmind/vision-perceiver-learned")
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
encoding = feature_extractor(image, return_tensors="pt")
inputs = encoding.pixel_values
outputs = model(inputs)
logits = outputs.logits
print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[logits.argmax(-1).item()])
>>> should print Predicted class: tabby, tabby cat
📚 Documentation
Model description
Perceiver IO is a transformer encoder model that can be applied on any modality (text, images, audio, video, ...). The core idea is to employ the self - attention mechanism on a not - too - large set of latent vectors (e.g. 256 or 512), and only use the inputs to perform cross - attention with the latents. This allows for the time and memory requirements of the self - attention mechanism to not depend on the size of the inputs.
To decode, the authors employ so - called decoder queries, which allow to flexibly decode the final hidden states of the latents to produce outputs of arbitrary size and semantics. For image classification, the output is a tensor containing the logits, of shape (batch_size, num_labels).
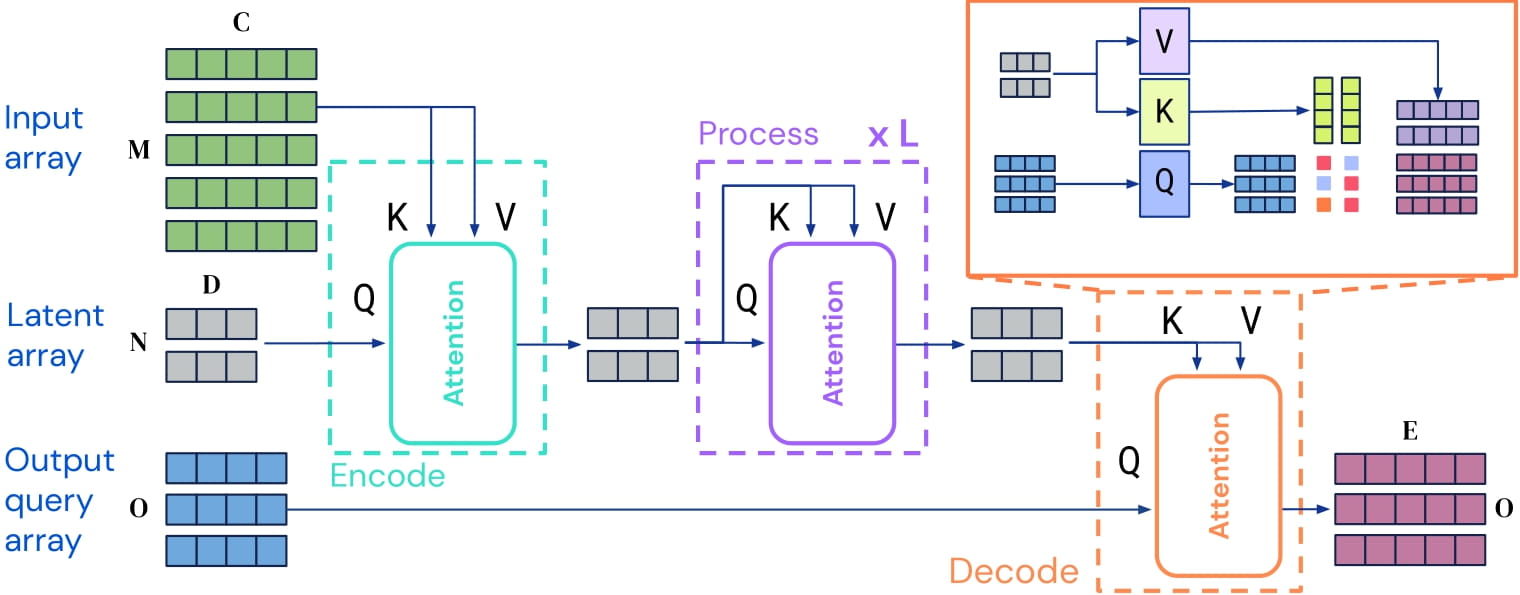
Perceiver IO architecture.
As the time and memory requirements of the self - attention mechanism don't depend on the size of the inputs, the Perceiver IO authors can train the model directly on raw pixel values, rather than on patches as is done in ViT. This particular model only adds learned 1D position embeddings to the pixel values, hence it is given no privileged information about the 2D structure of images.
By pre - training the model, it learns an inner representation of images that can then be used to extract features useful for downstream tasks: if you have a dataset of labeled images for instance, you can train a standard classifier by replacing the classification decoder.
Intended uses & limitations
You can use the raw model for image classification. See the model hub to look for other fine - tuned versions on a task that may interest you.
Training data
This model was pretrained on ImageNet, a dataset consisting of 14 million images and 1k classes.
Training procedure
Preprocessing
Images are center cropped and resized to a resolution of 224x224 and normalized across the RGB channels. Note that data augmentation was used during pre - training, as explained in Appendix H of the paper.
Pretraining
Hyperparameter details can be found in Appendix H of the paper.
Evaluation results
This model is able to achieve a top - 1 accuracy of 72.7 on ImageNet - 1k, despite having no privileged information about the 2D structure of images.
BibTeX entry and citation info
@article{DBLP:journals/corr/abs-2107-14795,
author = {Andrew Jaegle and
Sebastian Borgeaud and
Jean{-}Baptiste Alayrac and
Carl Doersch and
Catalin Ionescu and
David Ding and
Skanda Koppula and
Daniel Zoran and
Andrew Brock and
Evan Shelhamer and
Olivier J. H{\'{e}}naff and
Matthew M. Botvinick and
Andrew Zisserman and
Oriol Vinyals and
Jo{\~{a}}o Carreira},
title = {Perceiver {IO:} {A} General Architecture for Structured Inputs {\&}
Outputs},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/2107.14795},
year = {2021},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.14795},
eprinttype = {arXiv},
eprint = {2107.14795},
timestamp = {Tue, 03 Aug 2021 14:53:34 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/journals/corr/abs-2107-14795.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}
📄 License
This model is released under the Apache - 2.0 license.
| Property |
Details |
| Model Type |
Perceiver IO for vision with learned position embeddings |
| Training Data |
ImageNet (14 million images, 1,000 classes) |

