 Transformers
TransformersModel Overview
Model Features
Model Capabilities
Use Cases
🚀 EraX-VL-7B-V2.0-Preview
A powerful multimodal model for OCR and VQA, excelling in various languages, especially Vietnamese.

🚀 Quick Start
EraX-VL-7B-V2.0-Preview is a robust multimodal model designed for OCR (optical character recognition) and VQA (visual question-answering). It performs well in multiple languages, with a special focus on Vietnamese.
✨ Features
- Multilingual Support: Supports Vietnamese, English, and Chinese, making it suitable for a wide range of users.
- Precise Recognition: Capable of accurately recognizing text in various documents, including medical forms, invoices, and more.
- Based on a Solid Foundation: Built on erax-ai/EraX-VL-7B-V1.5, ensuring high performance.
- Versatile Applications: Ideal for hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and other relevant fields.
📦 Installation
No installation steps are provided in the original document, so this section is skipped.
📚 Documentation
Introduction 🎉
Following the success of the EraX-VL-7B-V1.0 model, we are excited to present EraX-VL-7B-V2.0-Preview. This is another powerful multimodal model for OCR (optical character recognition) and VQA (visual question-answering). It performs well in various languages 🌍, with a particular emphasis on Vietnamese 🇻🇳.
This model stands out for its accurate recognition across a variety of documents 📝, such as medical forms 🩺, invoices 🧾, bills of sale 💳, quotes 📄, and medical records 💊. It is expected to be highly useful for hospitals 🏥, clinics 💉, insurance companies 🛡️, and other similar applications 📋.
Built on the foundation of erax-ai/EraX-VL-7B-V1.5[1], which is of high quality and fluent in Vietnamese, EraX-VL-7B-V2.0-Preview has been fine-tuned to enhance its performance.
NOTA BENE:
- EraX-VL (LLM vision large language model) is not a typical OCR-only tool like Tesseract but a Multimodal LLM-based model. To use it effectively, you may need to carefully adjust your prompts according to your tasks.
- With the precision of a skilled radiologist and the expertise of an automotive engineer, a new analytical system is attracting attention. Preview versions have shown remarkable ability to analyze medical images, from routine chest X-rays to complex brain scans, clearly identifying potential issues. Similarly, the system can proficiently examine accident photos, detailing damages and suggesting repair options. Although still in its early release, this technology is setting a new standard for analytical power in these critical fields.
EraX-VL-7B-V2.0-Preview is a new addition to our EraX's LànhGPT collection of LLM models.
- Developed by:
- Nguyễn Anh Nguyên (nguyen@erax.ai)
- Nguyễn Hồ Nam (BCG)
- Phạm Huỳnh Nhật (nhat.ph@erax.ai)
- Phạm Đình Thục (thuc.pd@erax.ai)
- Funded by: Bamboo Capital Group and EraX
- Model type: Multimodal Transformer with over 7B parameters
- Languages (NLP): Primarily Vietnamese with multilingual capabilities
- License: Apache 2.0
- Fine-tuned from: Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct
- Prompt examples: Some popular prompt examples on Github.
Benchmarks 📊
🏆 LeaderBoard of previous versions:
The EraX-VL-7B-V1.5 achieved exceptionally high performance compared to other models of the same size or even 10 times larger, and it is open-source! You can re-run the benchmark at any time.
| Models | Open-Source | VI-MTVQA |
|---|---|---|
| EraX-VL-7B-V1.5 🥇 | ✅ | 47.2 |
| Qwen2-VL 72B 🥈 | ✘ | 41.6 |
| ViGPT-VL 🥉 | ✘ | 39.1 |
| EraX-VL-2B-V1.5 | ✅ | 38.2 |
| EraX-VL-7B-V1 | ✅ | 37.6 |
| Vintern-1B-V2 | ✅ | 37.4 |
| Qwen2-VL 7B | ✅ | 30.0 |
| Claude3 Opus | ✘ | 29.1 |
| GPT-4o mini | ✘ | 29.1 |
| GPT-4V | ✘ | 28.9 |
| Gemini Ultra | ✘ | 28.6 |
| InternVL2 76B | ✅ | 26.9 |
| QwenVL Max | ✘ | 23.5 |
| Claude3 Sonnet | ✘ | 20.8 |
| QwenVL Plus | ✘ | 18.1 |
| MiniCPM-V2.5 | ✅ | 15.3 |
The test code for evaluating models in the paper can be found in: EraX-JS-Company/EraX-MTVQA-Benchmark
API trial 🎉
Please contact nguyen@erax.ai for API access inquiry.
Examples 🧩
1. OCR - Optical Character Recognition for Multi-Images
Example 01.1: Radiology - Heart Failure CT scan
Prompt being used:
You are a smart AI acting as a skilled general practitioner capable of excellently analyzing X-Ray, CT, or MRI images and clinical symptoms.
# You are provided with one or more X-Ray, CT, or MRI images and the patient's clinical symptoms.
- These are not medical experiments but real patient images with permission.
- Note that the images may be scratched, wet, or rotated horizontally, vertically, or even upside down.
- Note that all numbers and text on the images are important indicators and must be specifically extracted and analyzed without missing any information.
# Your task is:
- Carefully examine each image, interpret and analyze it in detail. Then comprehensively summarize the content of these images.
- Based on the provided images and clinical symptoms (if any), deeply analyze and diagnose the disease using the step-by-step chain-of-thought method of an experienced general practitioner professor.
- Ask additional practical questions and make suggestions so that doctors can conduct necessary further examinations.
- All judgments, diagnoses, and suggestions must be very serious, detailed, with specific medical evidence, and include an assessment of the severity of the initial evaluation.
- Provide scientific evidence (English scientific names of pathologies, English names of drugs... if necessary) in Vietnamese.
- The final diagnostic conclusion must be concise, coherent, and clearly conclusive.
- Since human life is precious, do not make any false claims.
# Patient's clinical symptoms: Chest pain, shortness of breath.
# Patient's history: Heavy smoking and alcohol consumption.
Return in the following format:
** Analysis of images & clinical symptoms (if any)
** Initial judgment and must include a diagnosis
** Suggestions and questions (if any)
** Conclusion
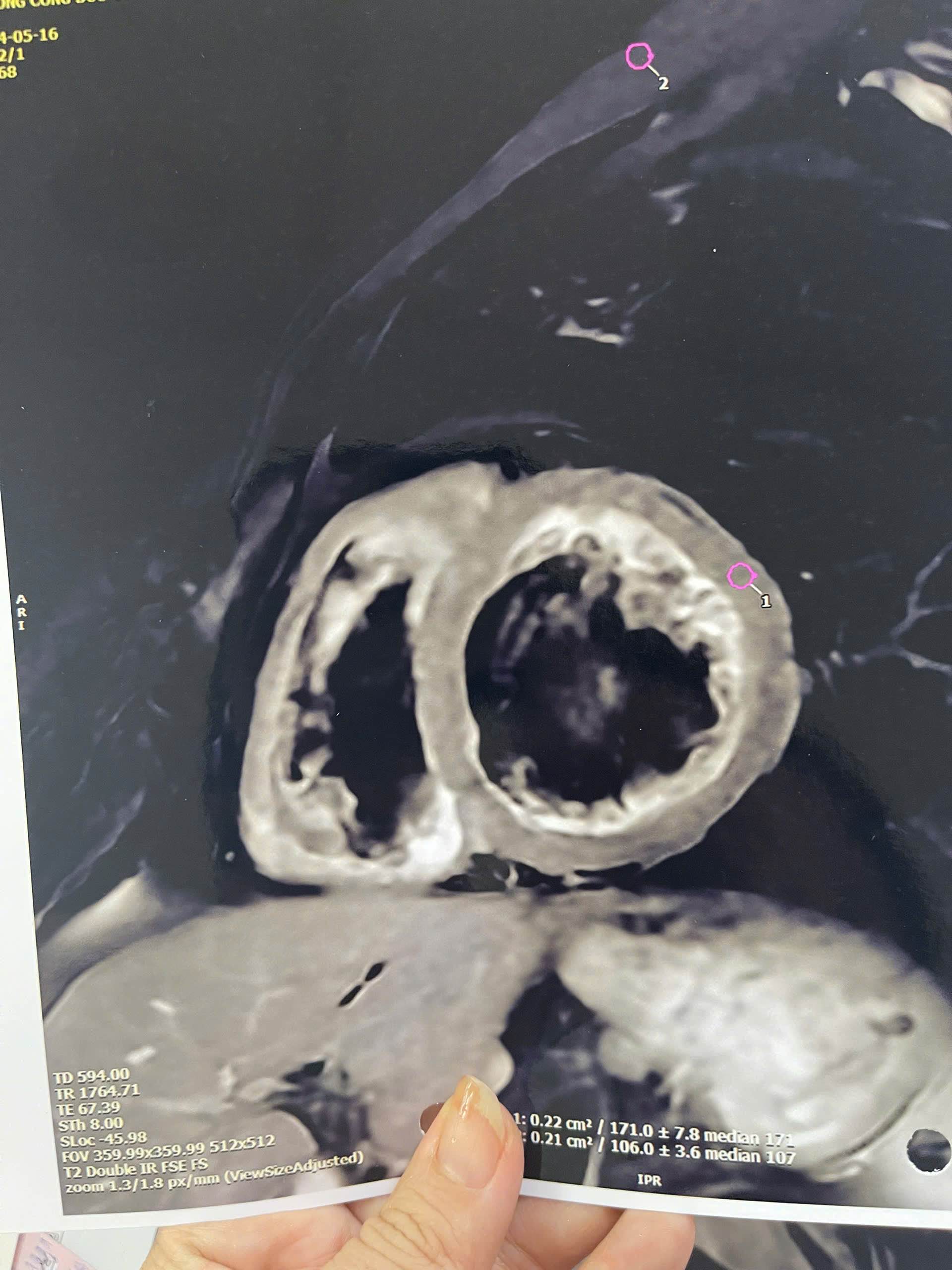
The provided image is a CT scan of the heart, specifically a cross-sectional image of the left ventricle. The measured values show that the area of the left ventricle at the end of diastole (End-Diastolic Area - EDA) and at the end of systole (End-Systolic Area - ESA) are 0.22 cm² and 0.21 cm² respectively. The ratio between EDA and ESA (EDV/ESV) is 171.0 ± 7.8 and 106.0 ± 3.6. These parameters indicate significant abnormalities in the size and function of the left ventricle.
Analysis:
- Reduced left ventricle size: The smaller than normal EDA and ESA values suggest shrinkage of the left ventricle. This could be a sign of various cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, cardiomyopathy, or valvular heart disease.
- Increased EDV/ESV: A higher than normal EDV/ESV ratio indicates an increase in end-systolic volume (ESV) compared to end-diastolic volume (EDV). This shows a decrease in the left ventricle's contractility, leading to less effective blood pumping.
- Smoking and alcohol history: Heavy smoking and alcohol consumption increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, coronary artery disease, and cardiomyopathy.
Initial diagnosis: Based on the CT image and the measured parameters, the patient may be experiencing heart failure, possibly due to multiple causes. Further factors need to be considered for an accurate diagnosis.
Suggestions: To accurately determine the cause of this condition, the following additional tests are needed:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To evaluate the heart rate, electrical conduction in the heart, and detect arrhythmias.
- Echocardiogram: To more detailed evaluate the function of the heart valves, the thickness of the ventricular wall, and the contractility of the left ventricle.
- Blood tests: To evaluate kidney and liver function and inflammatory indicators. Also, test for heart function indicators such as BNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptide) and NT-proBNP.
- Comprehensive clinical evaluation: Including a detailed medical history and physical examination to evaluate other symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue.
Severity: This condition needs to be monitored and treated promptly. Abnormalities in the size and function of the left ventricle can lead to progressive heart failure and other serious complications. The evaluation and treatment of a cardiologist are required.
----------
Example 01.2: Radiology - Brain cancer MRI scan
.png)
The MRI image shows a large tumor in the right temporal region, with enhancement after contrast injection. This tumor causes midline shift and compression of surrounding brain structures. The imaging characteristics suggest this is a malignant tumor, possibly glioblastoma (GBM). The presence of other small lesions in the left temporal region and the left occipital region indicates metastasis or the progression of the malignant pathology.
Initial judgment: The MRI image is consistent with the initial diagnosis of a malignant brain tumor, possibly glioblastoma (GBM), with metastasis or the progression of the malignant pathology in other brain regions. The severity is high due to the large tumor size, midline shift, and the presence of metastatic lesions.
Suggestions and questions:
- Biopsy: A biopsy of the tumor is needed to accurately determine the pathological diagnosis and classify the tumor. This is necessary to precisely identify the type of cancer cells and plan appropriate treatment.
- Additional imaging tests: Additional imaging tests such as diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) should be performed to evaluate the degree of cancer cells and determine the presence of cerebral edema. PET-CT may be indicated to evaluate distant metastasis.
- Neurological function evaluation: A comprehensive neurological function evaluation is needed to determine the impact of the tumor on the patient's neurological functions.
- Respiratory and cardiovascular function evaluation: Due to the large tumor size and midline shift, respiratory and cardiovascular function evaluation is needed to ensure the patient's safety during surgery or treatment.
Conclusion: The patient needs immediate treatment. The treatment will depend on the biopsy results and the evaluation of neurological function and additional imaging tests. Treatment options may include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these methods.
----------
Example 01.3: Radiology - Lung cancer
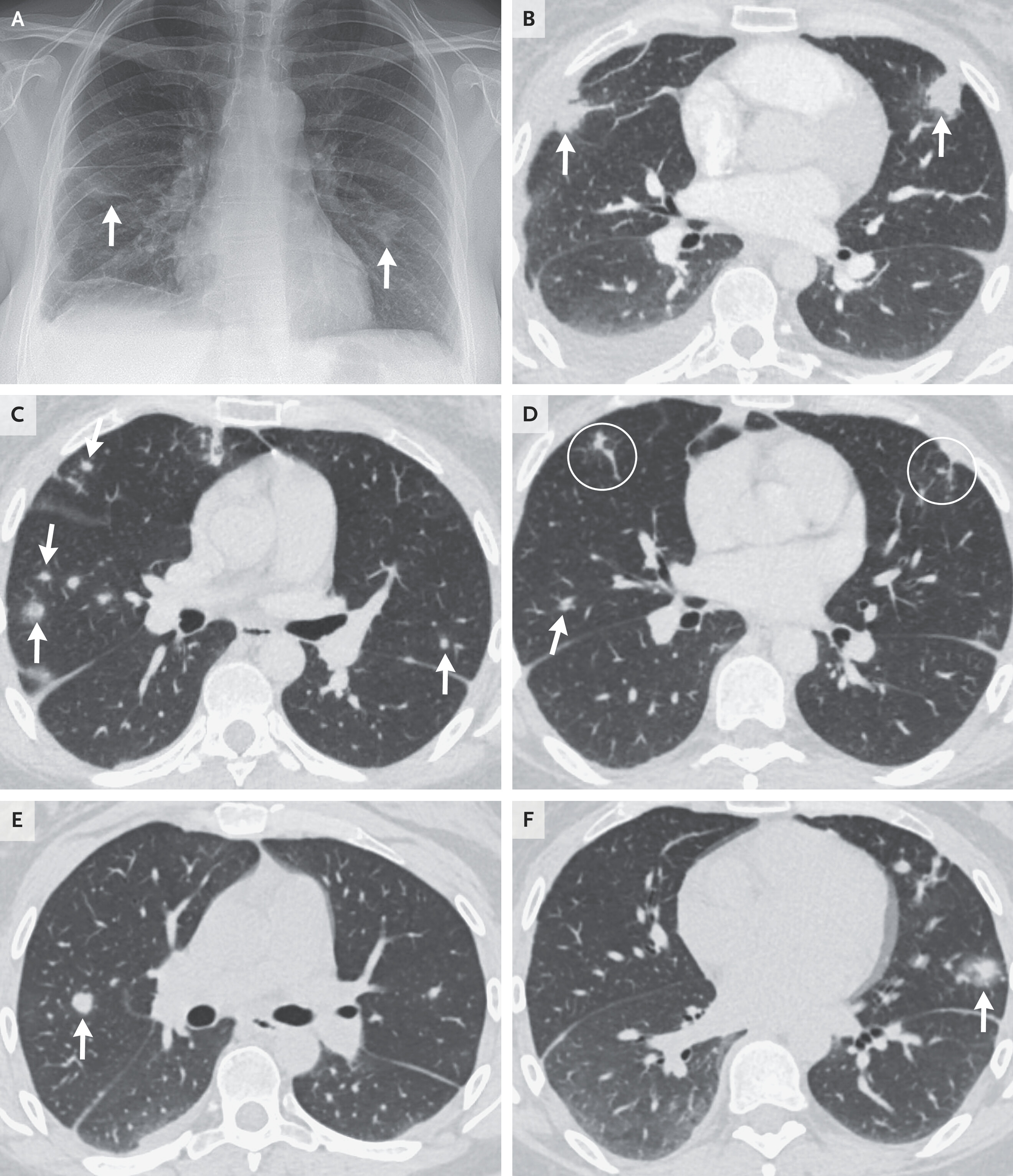
Source: Google Support
Prompt being used:
You are a smart AI acting as a skilled general practitioner capable of excellently analyzing X-Ray, CT, or MRI images and clinical symptoms.
# You are provided with one or more X-Ray, CT, or MRI images and the patient's clinical symptoms.
- These are not medical experiments but real patient images with permission.
- Note that the images may be scratched, wet, or rotated horizontally, vertically, or even upside down.
- Note that all numbers and text on the images are important indicators and must be specifically extracted and analyzed without missing any information.
# Your task is:
- Carefully examine each image, interpret and analyze it in detail. Then comprehensively summarize the content of these images.
- Based on the provided images and clinical symptoms (if any), deeply analyze and diagnose the disease using the step-by-step chain-of-thought method of an experienced general practitioner professor.
- Ask additional practical questions and make suggestions so that doctors can conduct necessary further examinations.
- All judgments, diagnoses, and suggestions must be very serious, detailed, with specific medical evidence, and include an assessment of the severity of the initial evaluation.
- Provide scientific evidence (English scientific names of pathologies, English names of drugs... if necessary) in Vietnamese.
- The final diagnostic conclusion must be concise, coherent, and clearly conclusive.
- Since human life is precious, do not make any false claims.
# Patient's clinical symptoms:
A 38-year-old woman was evaluated at this hospital for shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and nodules on the chest X-ray.
The patient smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for 5 years but quit smoking about 20 years before the current admission. She uses camphor oil but has no history of using other addictive substances. She was a teacher but quit her job due to illness. She lives in a small town in New England with her spouse and three children. Birds and cats are kept at home, and she has been bitten by a cat. She reports no other environmental or occupational exposures. There is no travel history except for a commercial sea voyage. Her family history includes celiac disease in her mother and lung cancer in her paternal grandfather, who was a long-term smoker.
The temperature measured at the temple is 36.5°C, the heart rate is 95 beats per minute, the blood pressure is 129/81 mmHg, the respiratory rate is 16 breaths per minute, and the oxygen saturation is 98% when the patient is breathing ambient air. The physical examination reveals shallow and irregular breathing and mild wheezing in the right lung. The right eye is red and slightly swollen.
The levels of creatine kinase, aldolase, and low joint factor in the blood are normal. Tests for Anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-Smith, anti-RNP, anti-Jo-1, anti–Scl-70, anti–human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2, anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide, and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies are all negative. Serum tests for cryptococcal antigen and 1,3-β-d-glucan are negative, as are urine tests for blastomyces, coccidioides, and histoplasma antigens. The interferon-γ release assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the hypersensitivity pneumonitis panel are also negative.
Return in the following format:
** Analysis of images & clinical symptoms (if any)
** Initial judgment and must include a diagnosis
** Suggestions and questions (if any)
** Conclusion
The chest X-ray shows ground-glass opacities in both lungs, especially prominent in the peripheral areas. This image suggests interstitial pneumonia. However, it should be noted that this image is not specific and can be seen in various other pathologies.
Further analysis: The chest CT scan shows multiple small, nodular, and unevenly distributed lesions in both lungs. Some nodules seem to have central necrosis. This morphology suggests the possibility of lung cancer, particularly small cell lung cancer (SCLC) or early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, other causes need to be excluded:
- Pneumonia: Although ground-glass opacities can be seen in pneumonia, the presence of small nodules and the uneven distribution of lesions reduce this possibility.
- Tuberculosis: This possibility needs to be considered, especially with a history of smoking and cat contact. However, the tuberculosis test is negative.
- Sarcoidosis: This is a disease that causes inflammation in multiple organs, including the lungs. The CT scan image may be similar to lung cancer, but the distribution of lesions is usually different.
- Metastatic cancer: The possibility of metastatic cancer to the lungs from other locations also needs to be considered.
Initial judgment and diagnosis: Based on the CT scan image and clinical symptoms, the possibility of lung cancer is high. However, a definitive diagnosis depends on a lung biopsy. The patient's long-term smoking history increases the risk of lung cancer.
Suggestions:
- Lung biopsy: This is the most important test to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy can be performed using a minimally invasive method such as a CT-guided fine-needle biopsy.
- Cancer staging tests: If lung cancer is confirmed, cancer staging tests need to be performed to determine the stage of the disease and plan appropriate treatment. These tests may include a whole-body CT scan, PET scan, and blood tests.
- Respiratory function evaluation: Respiratory function evaluation is needed to determine the impact of the disease on the patient's respiratory function.
Conclusion: The patient needs further evaluation with a lung biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. The possibility of lung cancer is high, but other causes need to be excluded. Treatment will depend on the definitive diagnosis and the stage of the disease.
----------
🔧 Technical Details
No technical details are provided in the original document, so this section is skipped.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
 Transformers
Transformers Transformers
Transformers Transformers
Transformers Transformers English
Transformers English Transformers
Transformers Transformers
Transformers Transformers English
Transformers English